EE 2212
EXPERIMENT 6
10 April 2014
Bipolar Junction
Transistor (BJT) Measurements, Circuit Analysis, And
Amplifier Operation
COMPONENTS
Report is due on
Wednesday, 27 November. This is report
will be evaluated on a 20 Point Scale.
2N3904 or 2N2222 npn transistor
Resistors: 5kW and 100kW
Note: Use the 2N3904 or 2N2222 npn transistor device models in SPICE rather than the
default model
DC Bias Analysis
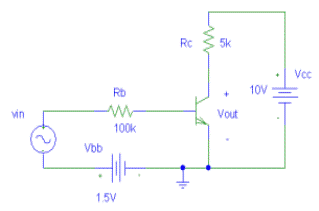
Construct the circuit in Figure 1. Use = 10
Volts for the DC supply. Measure and record the Q-Point values of IB,
IC, VBE, and VCE. One of many measurement approaches is to measure the voltage
across the RB and RC resistors to obtain the current rather than inserting an
ammeter in series. Be sure you measure
the actual resistor values for your measurement to obtain more accurate
results. Compare your results with a
SPICE analysis of this circuit. Use the 2N3904 or 2N2222 in
the SPICE library. The signal source vin(t) should be set to zero for this portion of
the experiment. You may have to adjust
VBB = 1.5 volts and/or Rb to obtain a Q-Point in the forward-active
region because of the potentially wide variation of BJT β values. You will want to use the actual values in
your SPICE simulations. Note the ability
of SPICE to provide Q-Point information.
Demonstrate
Small-Signal and Large-Signal Operation
Now set vin(t) for a 1 kHz sine wave from the function
generator. Adjust the amplitude initially
to 0.5 Volts (1 VPeak-to-Peak), Measure the voltage
gain. Simulate the circuit in SPICE with
your transistor using a transient analysis.
Explain your results in the context of a load-line analysis. Use the small-signal model to compute the
voltage gain. Also show the transfer
characteristic. Adjust vin(t) to demonstrate
clipping.
Another
classic math joke if can handle it!
My computer uses WINDOWS 8 and the Dilbert cartoon
expresses my feelings about software upgrades!
I will miss WINDOWS XP.
