EE
2212
PROBLEM
SET 5
S.
G. Burns
Due: Monday, 8 November
EXTRA CREDIT OPPORTUNITY
Up to 30 Points added to your
end-of-the-semester Quiz Point Total. How do you earn this? I want
circuit diagrams and specifications for power amplifiers and
related equipment that you may have for some of your “stuff” and is usable,
that is, supports ZOOM in-class discussions when we get to power
amplifiers towards the end of the semester. Information such as circuit
diagrams, specifications for your sound systems,
guitar amps, car stereos, powered sub-woofers, associated power supplies,
speaker systems, etc. Could be solid-state or vacuum tube based. I define power loosely in that information on
your portable electronics such as wireless earbuds, smart phones, tablets, etc.
also is interesting to me and appropriate for class discussion. Homebrew
projects in these categories
are appropriate. I would
like to borrow the material to supplement our class discussions on power
amplifier circuits. Do not
just go to the WEB for information that doesn’t relate directly to stuff
you or your parents have. Hard Deadline for
receipt of materials is to be sent to me as an e-mail attachment (PPT or PDF)
by Monday, 22 November, 4 pm. NO EXCEPTIONS!!! Earlier is better so I
can do a decent scheduling job.! Be sure your name is in the
submitted materials. I will award up to 30 points based upon
relevance and class usability and YOU describing
the item and technical information to the class.
Your 3-5 minute presentation via a ZOOM share will be scheduled for Friday
or Monday, (3 or 6 December). Feel free if to discuss what you have with me if you have
questions. The meaner and badder stuff, the better.
The following problems provide practice in working with small-signal
models. Use the basic voltage-controlled current generator FET small-signal
model with λ (Lambda) =0. In
addition to answering the text questions, you are to draw and label the
resultant small-signal model circuit diagrams.
Express your derivations symbolically; that is no calculations are
required. These
problems also will familiarize you with the text FET symbol
notation variations. It is important
that you label circuit nodes carefully.
1. Draw the small-signal model for Figure
P13.5. After you have obtained the
small-signal model, derive an equation for the voltage gain defined by av
= vo/vi.
Observe that no numerical calculations
are required. Note that this circuit
uses an NMOS. This circuit is a
common-source.
2. Draw the small-signal model for Figure
P13.8. After you have obtained the
small-signal model, derive an equation for the voltage gain defined by av
= vo/vi.
Observe that no numerical calculations are required. Note that this circuit uses a PMOS. This circuit is a common-source.
3. Draw the small-signal model for Figure P13.9. After you have obtained the small-signal
model, derive an equation for the voltage gain defined
by av = vo/vi. Observe that no numerical calculations are
required. Note that this circuit uses an
NMOS. The circuit
is a common-gate.
4.
Small-Signal Model derivation for a cascade amplifier excerpted from an old quiz.

(a) Sketch and label a small-signal model for this
circuit which consists of two Common Source amplifiers in a cascade
configuration. Assume all capacitors are
large at the frequency of interest . Your model should be complete and
well-labeled. Assume λ= 0.
(b) Derive an expression for the voltage gain defined by Av = Vout/Vs . Observe no
numerical calculations are required.
5. Synthesize a Resistor With A Switched Capacitor Circuit
Design a switched capacitor circuit that could be used to
synthesize a 20 kW
resistor where the high frequency band
limit, of any signals passing the equivalent synthesized resistor, is in the range expected from your audio
band-limited smart phone. I will accept
any reasonable number for what you consider the highest frequency for speech
one could expect from your smart phone .
Your design should include:
· Well-labeled circuit diagram
· Design equations with key component values and an
appropriate clock frequency.
· Clock waveforms .
6. Switched Capacitor Low Pass Filter Design (again excerpted
from an old quiz)
Use the basic concepts from the equivalent
resistor design discussed in class , design a switched
capacitor LPF that replaces the analog LPF; a topology we studied extensively
the first couple of weeks of the semester.
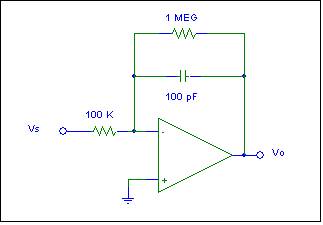
Design this circuit as a switched capacitor low-pass filter.
Your design should include:
· Well-labeled
circuit diagram.
· No
resistors-That is replace the two resistors with two switched capacitors and
four FETs. Your design should include appropriate W/L ratios for the four
FETs. An appropriate clock frequency for
operation at input signal frequencies to 5 kHz.
· Key
clock waveforms with the correct phasing for the four FETs illustrating the
operation.
It’s
all Greek to me

Alternate
definition for dynamic range.

Registration for your Spring
2022 classes is
upon us!!! The following are dedicated
to those of you
wanting to register for your breadth technical
elective.
For Those of You Planning to take Electromagnetics
(EE 3445)

And We Don’t Want To Forget the CprE/CS Minor
To Support the Energy Engineering Minor

And Also Consider the Math Minor

And there is always a UROP and Senior
Design!



