EE 2212
PROBLEM SET 4
S. G. Burns
Due:† Monday, 25 October 2021
NOTE
1:† QUIZ 4 might also include a few
basics related to photovoltaics and LED lighting.† Your QUIZ 4 grades will be much better if you
study the Photonics Supplement.
1. Text
Problem 4.1 and 4.2 as a combination† (Look at Figure 4.2 for guidance† For Text 4.2, observe that is Cox,
capacitance/unit area.† Watch your
units.† Usually farads/cm2 are
preferred for Cox units.† When the text
and in industry talks about an MOS capacitor, they are usually referring to
Cox. ††The total capacitance is then
obtained by multiplying by (W x L).† This
idea of scaling is very important in VLSI circuit design.† The parallel plate basic capacitor model
works very well in VLSI design.† We will
soon discuss how this plays into imaging and display applications.
2. Text
Problems 4.4 and 4.8 for NMOS and Text †Problem†
4.47 for PMOS† Some additional
basic calculations to provide experience in units and nomenclature.† Organize your results in a table.† Page 160 (NMOS) and 161 (PMOS) has a table
defining the relationships for key FET model parameters.†
3.
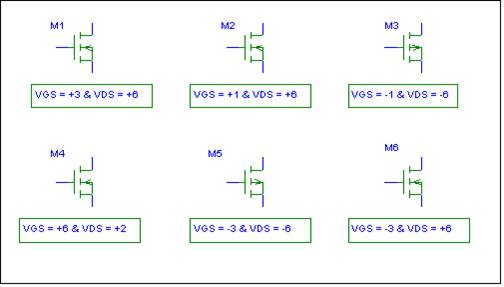
From an old quiz.†
Regions of operation are very important in circuit design using
MOSFETS.† Extracted from an old
quiz.††† For the indicated ††††††††† bias conditions, state whether the FET
is operating in the OHMIC (TRIODE) region, SATURATION region, or CUTOFF
region.† Explain your reasoning.†† Assume that |VT | = 2† volts for both the
NMOS and PMOS enhancement mode transistors.†
M1 __________††††††††††††† M2
__________††††††††††††††† M3
__________††††
M4 __________††††††††† M5
__________††††††††† M6 __________
4.
Figure† P4.18 NMOS
Characteristics†† Generate a SPICE NMOS
model by modifying the default NMOS transistor model (MBREAKN in PSPICE ) or the
equivalent in LT SPICE that will reasonably match the curves in P4.18
figure.† If you look at the curves, it is
a good assumption that λ = 0.† Your
problem submission must include the listing of your modified MOS parameters and
the resultant ID-VDS curves and the SQRT(ID) versus† VGS
curve.
This is what
we use for blocking dc and passing ac in many discrete device amplifier
circuits.††† Synonymous with coupling
capacitor.† Also a dc blocking capacitor
is employed in your oscilloscope when switching to AC input using the soft
keys.†

Consider the signal swing around the Q-Point which established the
dynamic range of a circuit†
which we will use in amplifier design

Even though most of you are EE students, there is some
information you can use from CS I.† Of
course, you can always dive deeper into CS but it messy in more ways than one,
refer to the figure.† I donít know if
this diagram is covered in more advanced CS courses if you decide to work on a CS
or CprE Minor.†
Can you tell that I am a hardware guy!