|
|
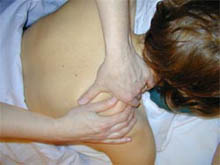 Therapeutic massage |
According
to studies done at Yale and Rutgers Universities, the best predictor of
well being and future health is one's current opinion regarding their
health status. If one feels they are well, their likelihood of being well
in the future is significantly greater. An attempt to quantify the scientific
underpinnings of these findings has resulted in the birth of the field
of psychoneuroimmunology. This is an attempt to explore the interactions
between the psychological, the neurological and the immunological aspects
of the patient. This reviewer would suggest that even this is a narrow
view of the topic in light of recent research findings. Most of the neurotransmitters
are manufactured in the gut and many of the gut modulating hormones are
manufactured in the brain. By incorporating aspects of the GI system,
and likely, many other systems in the body, this would give a more complete
picture of mind/body interaction. I call this psycho-neuro-cardio-gastro-endocrino-musculo-respiro-skeletal-integumento-exocrino-etcetero-immunology!
|
|
For questions, please contact Terry Estep |
|
The
University of Minnesota Duluth is an equal opportunity educator and
employer. |